Data privacy is now a front-line issue for businesses of every size. Companies are gathering more personal information than ever before and more than 72 percent of employees still work solely on-site. But the flood of data is not the biggest threat. The real challenge is what happens when technology gets ahead of privacy, raising questions that tools alone cannot answer. This changes everything about how organizations build trust and define responsibility in a digital world.

Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
| Data Privacy is Essential | Protecting personal information is key for trust and compliance in business
practices. |
| Implement Strong Data
Protection Strategies |
Develop comprehensive measures that include technical and procedural
safeguards around data handling. |
| Continuous Employee
Training is Crucial |
Ongoing education on data privacy helps cultivate an organizational culture
committed to protecting personal data. |
| Balancing Automation and
Privacy is Key |
Organizations must respect privacy while leveraging automated technologies
through responsible data management. |
| Stay Updated on Evolving
Regulations |
Adapting to changing laws and practices is vital for effective data privacy
management and compliance. |
Understanding Data Privacy and Its Importance
Data privacy represents a critical foundation for protecting personal information in our increasingly digital world. At its core, data privacy ensures individuals retain control over their sensitive personal details and how organizations collect, use, and share this information.
The Core Principles of Data Privacy
Understanding data privacy requires recognizing its fundamental principles. According to the Federal Trad e Commission, data privacy involves handling personal information responsibly and transparently. This means businesses must implement robust mechanisms that respect individual rights and prevent unauthorized access or misuse of personal data. Key principles include consent, transparency, and individual control. When businesses collect data, they must obtain clear permission from individuals, explain exactly how the information will be used, and provide mechanisms for people to access, modify, or delete their personal information. These principles are not just ethical guidelines but critical legal requirements in many jurisdictions. To provide a clear overview, the table below summarizes the core principles of data privacy as highlighted in the article, outlining their definitions and relevance for businesses.
| Principle | Definition | Business Relevance |
| Consent | Obtaining clear permission to collect data | Ensures lawful data processing and builds user
trust |
| Transparency | Clearly explaining data use to individuals | Promotes accountability and meets regulatory
requirements |
| Individual
Control |
Allowing people to access, modify, or
delete their data |
Empowers users and aligns with ethical and legal
responsibilities |
Why Data Privacy Matters for Modern Businesses
In the contemporary digital ecosystem, data privacy is more than a compliance checkbox. According to NIST, privacy engineering has become essential for organizations seeking to build trust and mitigate potential risks. Companies that prioritize data privacy demonstrate respect for their customers and protect themselves from potential legal and reputational damages. Businesses face significant consequences for data privacy failures. These can include substantial financial penalties, loss of customer trust, and potential legal action. By proactively implementing strong data privacy measures, organizations can safeguard their reputation and create a competitive advantage in an increasingly privacy-conscious marketplace.
Protecting Personal Information in a Connected World
Modern technology has transformed how personal information is collected and used. From social media platforms to e-commerce websites, digital interactions generate vast amounts of personal data. This makes robust data privacy practices not just recommended but absolutely necessary. Effective data privacy strategies involve multiple layers of protection. This includes secure data storage, encryption technologies, regular security audits, and comprehensive employee training on handling sensitive information. Organizations must also stay updated on evolving regulations and technological advances that impact data protection. Individuals and businesses alike must recognize that data privacy is a shared responsibility. While companies must implement strong protective measures, individuals must also remain vigilant about the information they share and understand their rights regarding personal data.
Data privacy is not a static concept but a dynamic field continuously evolving with technological advancements. As artificial intelligence, machine learning, and interconnected systems become more sophisticated, the strategies for protecting personal information must also adapt and improve.
Types of Data Collected in Modern Workplaces
Modern workplaces collect an extensive range of data across multiple dimensions, transforming how organizations understand and manage their workforce. This data collection spans digital interactions, physical workplace activities, and employee performance metrics. The following table organizes the major types of data collected in modern workplaces, including their examples and purposes as discussed in the article.
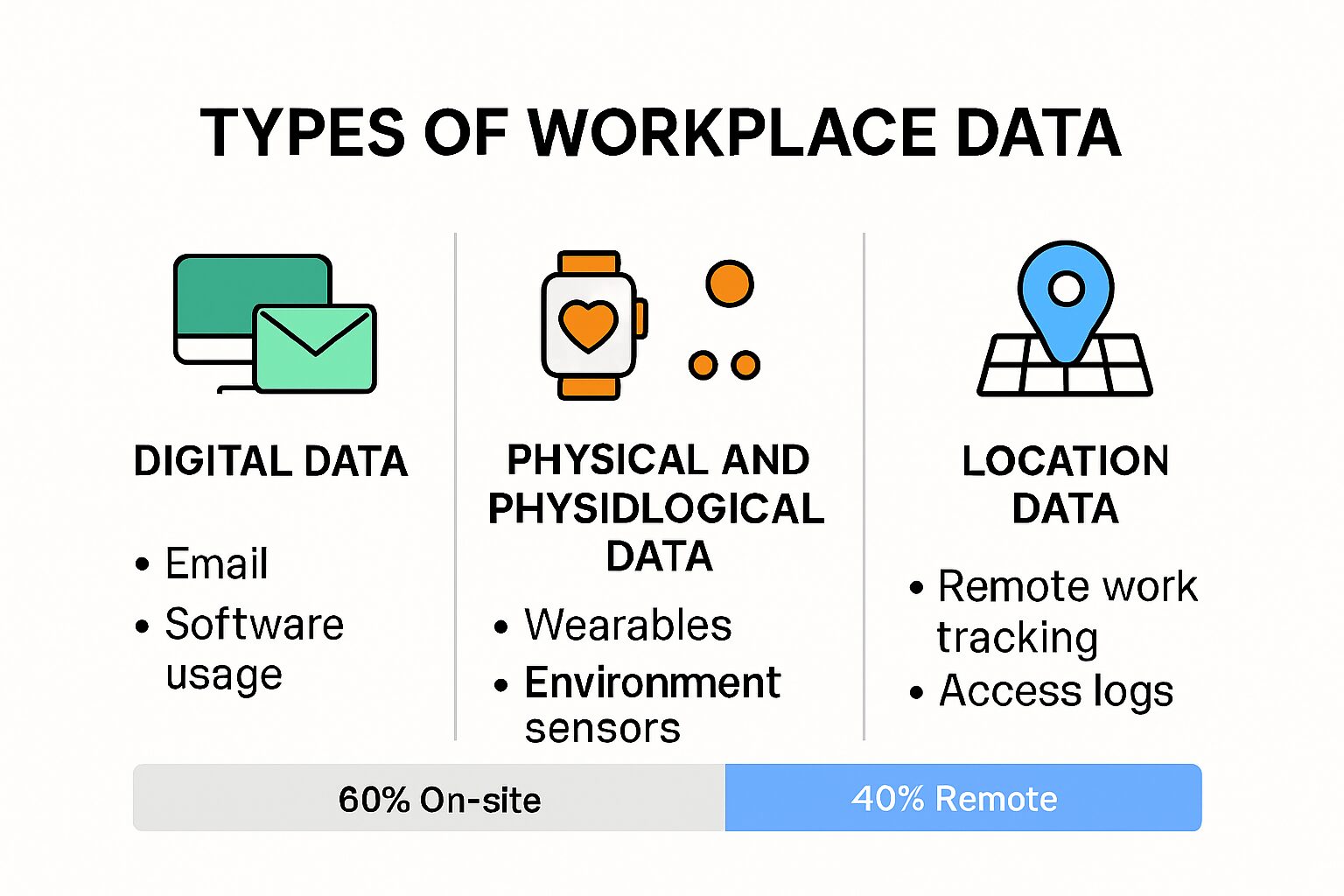
| Data Type | Examples | Purpose |
| Digital Workplace
Data |
Email metadata, software usage, login
times |
Analyze workflow, productivity, and
collaboration |
| Physical/Performance
Data |
Wearable device output, stress levels,
task metrics |
Enhance safety, track performance,
assess productivity |
| Location/Work
Arrangement |
On-site status, remote work logs,
geolocation, access |
Optimize workspace, monitor attendance,
inform policies |
Digital Workplace Data Collection
In the digital realm, employers gather substantial information about employee activities and interactions. According to Brookings Institution, companies now utilize sophisticated technologies to monitor computer usage, email communications, and digital workflow patterns. These digital tracking methods provide insights into productivity, collaboration, and resource utilization.
Typical digital data collection includes email metadata, website browsing history, login times, software usage duration, and communication platform interactions. Project management tools, communication platforms, and enterprise software generate rich datasets that help organizations analyze workflow efficiency, identify bottlenecks, and optimize team performance.
Physical and Performance Data Tracking
Workplace data collection extends beyond digital interactions. Research from arXiv highlights emerging workplace technologies that collect physiological and environmental data through wearable devices and advanced monitoring systems. These technologies track physical activity, environmental conditions, and even employee stress levels to enhance occupational safety and productivity. Performance tracking involves collecting metrics such as project completion rates, task efficiency, client interaction quality, and individual contribution assessments. Many organizations use comprehensive performance management systems that compile quantitative and qualitative data to evaluate employee contributions and potential.
Location and Work Arrangement Data
With evolving work models, employers are increasingly collecting data about work locations and arrangements. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates significant variations in workplace configurations, with 72% of employees working exclusively on-site, 11.4% working exclusively from home, and 9.1% adopting hybrid arrangements.
Here is a statistics table that organizes the workplace arrangement data mentioned in the article for easy reference. Location data collection includes remote work tracking, geolocation information for mobile workers, building access logs, and time spent in different workplace zones. These datasets help organizations optimize workspace utilization, understand employee movement patterns, and develop more flexible work policies. The proliferation of data collection technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. While these tools offer unprecedented insights into organizational dynamics, they simultaneously raise critical privacy and ethical considerations. Modern businesses must balance the potential benefits of comprehensive data collection with robust privacy protections and transparent communication about data usage practices.
Essential Data Privacy Practices for Organizations
Data privacy is not a one-time implementation but a continuous, strategic process that requires comprehensive and proactive approaches. Organizations must develop robust frameworks that protect sensitive information while maintaining operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
Developing Comprehensive Data Protection Strategies
According to the Federal Trade Commission, organizations must implement multiple layers of data protection. This involves creating a holistic approach that encompasses data collection, storage, access, and disposal practices.
| Work Arrangement | Percent of Employees |
| On-site Only | 72% |
| Work from Home Only | 11.4% |
| Hybrid | 9.1% |
Key strategic elements include:
- Data Minimization: Collecting only essential information required for specific business purposes
- Access Control: Limiting data access to authorized personnel
- Encryption: Protecting data through advanced technological safeguards
- Regular Risk Assessments: Continuously evaluating potential vulnerabilities
Improving data privacy requires understanding that protection is not just a technical challenge but a comprehensive organizational commitment. Every department must recognize its role in maintaining robust privacy standards.
Implementing Technical and Procedural Safeguards
The National Institute of Standards and Technology recommends implementing sophisticated technical controls to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. These controls go beyond basic security measures and require sophisticated technological and procedural approaches. Effective safeguards include multi-factor authentication, advanced network segmentation, real-time monitoring systems, and comprehensive incident response protocols. Organizations must also develop clear procedures for handling potential data breaches, ensuring rapid and effective communication and mitigation strategies.
Continuous Training and Organizational Culture
The International Association of Privacy Professionals emphasizes that successful data privacy extends beyond technological solutions. Creating a privacy-aware organizational culture is crucial for long-term protection. This involves regular employee training programs that go beyond annual compliance seminars. Effective privacy education should be ongoing, interactive, and tailored to different roles within the organization. Employees must understand not just the rules but the underlying principles of data protection and their personal responsibilities.

Organizations must also establish clear accountability mechanisms. This includes appointing dedicated privacy officers, creating transparent reporting channels for potential privacy concerns, and integrating privacy considerations into performance evaluations and corporate governance. The landscape of data privacy is dynamic and complex. As technologies evolve and regulatory environments become more sophisticated, organizations must remain adaptable. A successful data privacy strategy is not about achieving a static state of security but maintaining a flexible, responsive approach that can quickly address emerging challenges and technological innovations.
Balancing Automation and Data Privacy
Balancing automation and data privacy represents one of the most complex challenges facing modern organizations. As technological capabilities advance, businesses must navigate the delicate intersection between leveraging powerful automated systems and protecting individual privacy rights.
The Technological Tension of Automation and Privacy
Automation technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for efficiency and insights, but they simultaneously raise significant privacy concerns. According to IEEE, advanced surveillance technologies create fundamental challenges in maintaining individual privacy while achieving organizational objectives. Modern automation systems collect and process vast amounts of personal data to generate actionable insights. Machine learning algorithms, artificial intelligence platforms, and predictive analytics tools require extensive data inputs to function effectively. This creates an inherent tension between technological capability and privacy protection.
Strategic Approaches to Privacy-Preserving Automation
Organizations must develop nuanced strategies that enable technological innovation while respecting privacy boundaries. The National Academy of Public Administration emphasizes the critical importance of maintaining public trust through responsible data management.
Key strategic considerations include:
- Data Anonymization: Removing personally identifiable information before processing
- Consent Management: Implementing transparent opt-in and opt-out mechanisms
- Limited Data Access: Restricting automated systems to only essential information
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly auditing automated data processing systems
Effective privacy-preserving automation requires a proactive approach that anticipates potential privacy risks and builds protective mechanisms directly into technological infrastructure. This means designing systems with privacy considerations as a fundamental architectural requirement, not an afterthought.
Ethical Frameworks for Responsible Automation
Developing ethical frameworks becomes crucial as automation technologies become increasingly sophisticated. Organizations must establish clear guidelines that prioritize individual privacy while enabling technological innovation. This involves creating comprehensive policies that address data collection, processing, storage, and deletion.
Employees at all levels must understand the ethical implications of automated systems. Training programs should focus not just on technical capabilities but on the broader societal and individual impacts of data-driven technologies. Fostering a culture of responsible innovation requires ongoing education and critical reflection. The future of automation and privacy is not about choosing between technological advancement and individual rights. Instead, it demands a collaborative approach that recognizes the intrinsic value of both technological capabilities and personal privacy. Learn more about our approach to privacy-preserving technologies. As automation technologies continue to evolve, organizations must remain adaptable, transparent, and committed to ethical data practices. The most successful businesses will be those that can leverage technological capabilities while maintaining the highest standards of privacy protection and individual respect.
Turn Data Privacy Risks Into Your Competitive Edge
Every day, your business faces growing challenges around managing sensitive data and enforcing privacy policies. As highlighted in our guide above, balancing automation with data privacy and staying ahead of compliance risks can feel overwhelming. Relying on outdated or generic solutions puts your information and your reputation at risk.
Now is the time to secure your operations with award-winning AI technology that is designed specifically for privacy-first organizations. Polygraf AI offers locally deployed Small Language Model AI tools that help you identify AI or deepfake threats, enforce compliance automatically, and prevent costly code leaks or adversarial attacks. Discover how our trusted solutions can transform your privacy program from a vulnerability into a business advantage. Take action today and see why Polygraf AI is recognized across the industry for AI governance and advanced data protection. Ready to protect your sensitive data while powering responsible automation? Visit Polygraf AI now to learn more and schedule a personalized consultation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is data privacy?
Data privacy refers to the management and protection of personal information collected by organizations. It ensures individuals have control over their data and how it is used, shared, or accessed.
Why is data privacy important for modern businesses?
Data privacy is crucial for building trust with customers, complying with regulations, and protecting against legal and reputational risks. A strong emphasis on data privacy can also provide a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
What are some essential practices for data privacy in organizations?
Essential practices include developing comprehensive data protection strategies, implementing technical and procedural safeguards, and ensuring continuous employee training on data privacy principles and responsibilities.
How can businesses balance automation with data privacy?
Businesses can balance automation and data privacy by employing strategies such as data anonymization, consent management, restricting data access, and continuously monitoring automated systems to ensure compliance with privacy standards.