The cybersecurity landscape has changed. Old-school network defenses just aren’t cutting it anymore. Yet even with advanced firewalls, many companies are still blindsided when attackers slip past the perimeter. The shocking part is that Zero Trust security can reduce the impact of a data breach by up to 50 percent compared to traditional models. Most people think strong security means more walls but Zero Trust is a complete shift in mindset. It treats every access attempt as a potential threat, regardless of its origin. This changes everything about how we protect sensitive data.
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
| Adopt a Zero Trust Approach | Treat every access attempt as suspicious, verifying all users and devices before granting access. |
| Implement Least Privilege Access |
Limit user permissions to only what is necessary, minimizing potential damage from breaches. |
| Continuous Monitoring is Essential |
Establish real-time tracking systems to identify and respond to suspicious activities instantly. |
| Enhance Organizational Visibility |
Improve threat detection capabilities by gaining comprehensive insights into all network interactions. |
| Adapt Security Strategies Continuously |
Shift your security framework to dynamically adjust to evolving threats and business needs. |
Zero Trust Security Explained Simply
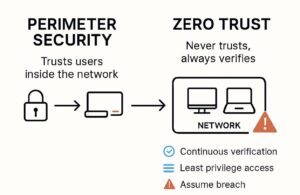
Zero Trust security represents a revolutionary approach to cybersecurity that fundamentally transforms how organizations protect their digital assets. Unlike traditional security models that rely on perimeter defenses, The core idea behind Zero Trust is simple: Forget perimeter defenses and embrace a ‘never trust, always verify’ mentality.
The Core Philosophy of Zero Trust
Traditional network security models assume that everything inside an organization’s network can be trusted. This approach is like having a castle with strong walls but no internal security. Zero Trust flips this paradigm completely. According to CISA, Zero Trust is an approach where no user or device is automatically trusted, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organizational network.
The fundamental mindset shift is treating every access attempt as potentially suspicious. This means every user, every device and every connection must prove its legitimacy before gaining access to any resources. Think of it like an airport security checkpoint where everyone goes through screening, regardless of their previous clearance or appearance.
Key Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
NIST’s Zero Trust Architecture outlines several critical principles that define this security model:
- Continuous Verification: Authentication is not a one-time event but an ongoing process
- Least Privilege Access: Users and systems receive only the minimum access required to perform their specific tasks
- Assume Breach: Always operate with the assumption that a security compromise is possible or already occurring
By implementing these principles, organizations create a dynamic security environment that adapts continuously. Instead of relying on static network boundaries, Zero Trust security focuses on protecting individual resources, monitoring every interaction and maintaining granular control over access.
In practice, this means sophisticated authentication methods like multi-factor authentication, real-time monitoring, and advanced analytics become standard practice. Each login, data request and system interaction is scrutinized, logged and validated before permission is granted. The beauty of Zero Trust is its holistic approach. It doesn’t just protect against external threats but also mitigates risks from insider threats, compromised credentials, and lateral movement within networks. By treating every request as potentially dangerous, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to sophisticated cyber attacks.
How Zero Trust Protects Businesses
Zero Trust completely transforms business protection by reimagining how organizations defend their digital assets. Rather than relying on traditional perimeter defenses, Zero Trust provides a comprehensive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity that addresses modern complex threat landscapes.
Reducing Attack Surface and Minimizing Risk
According to the U.S. Government Accountability Office, Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) prevents users, processes and devices from moving freely throughout a network after gaining access. This strategic limitation significantly reduces potential damage from security incidents. By implementing strict access controls and continuous verification, businesses can effectively contain potential breaches before they spread across critical systems.
Businesses face unprecedented cybersecurity challenges with increasingly sophisticated attack vectors.The U.S. Department of Commerce emphasizes that Zero Trust reduces data breach risks by implementing principles like least privilege access and continuous verification. This means every digital interaction is scrutinized, authenticated, and monitored in real-time.
Enhanced Visibility and Threat Detection
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) highlights that Zero Trust dramatically improves organizational visibility into network activities. CISA’s research demonstrates how Zero Trust enables more sophisticated threat detection and rapid response mechanisms. Key protective strategies include:
- Granular Access Controls: Restricting user permissions to only essential resources
- Continuous Authentication: Verifying user identity throughout their session
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Tracking and analyzing all network interactions
These strategies create a dynamic security environment where potential threats are identified and neutralized before they can cause significant damage. By treating every access attempt as potentially suspicious, businesses transform their cybersecurity from reactive to proactive. Zero Trust goes beyond traditional security models by recognizing that threats can emerge from both external and internal sources. Whether it’s a sophisticated cyber attack, a compromised employee credential or an unintentional insider mistake, Zero Trust provides a robust framework for comprehensive protection. For modern businesses operating in increasingly complex digital ecosystems, Zero Trust is not just a technology solution but a strategic approach to managing cybersecurity risks. It acknowledges that traditional network boundaries are obsolete and provides a flexible, intelligent framework for protecting critical digital assets in an era of constant technological change.
Steps to Implement Zero Trust Security
Putting Zero Trust into practice requires a strategic and comprehensive approach that transforms an organization’s cybersecurity ecosystem. This journey is not about implementing a single solution but creating a holistic security ecosystem that continuously verifies and protects digital assets.
Assessment and Asset Mapping
According to the SANS Institute, the first critical step in Zero Trust implementation is comprehensive asset identification and mapping. Organizations must develop a complete inventory of all digital resources, including hardware, software, data repositories and network infrastructure. This means understanding exactly what assets exist, how they interconnect and their potential vulnerabilities.
Key activities in this initial phase include:
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential security weaknesses and critical access points
- Asset Inventory & Classification: Catalog all hardware, software, data and accounts; classify by sensitivity.
- Data Flow Mapping: Map data movement across systems and third parties; highlight risks and weak points.
- User & Role Analysis: Audit access against least privilege; flag excessive or orphaned accounts.
- Third-Party & Vendor Risk Review: Document external integrations and SaaS use; assess partner risk exposure.
- Compliance Gap Analysis: Compare practices against regulations; identify non-compliance gaps.
- Baseline Security Posture Assessment: Evaluate monitoring, authentication and endpoint security as a pre–Zero Trust benchmark.
Implementing Least Privilege Access Controls
CISA’s Zero Trust Maturity Model emphasizes the critical importance of implementing strict access controls. Least privilege access means users are granted the minimum level of system permissions necessary, just to complete their specific tasks. This approach dramatically reduces potential attack surfaces by limiting potential damage from compromised credentials.
Effective implementation involves:
- Role-Based Access: Configuring permissions based on specific job functions
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Requiring multiple verification methods for access
- Dynamic Permission Management: Continuously adjusting access rights based on context and behavior

Continuous Monitoring and Adaptive Security
To help visualize the recommended Zero Trust implementation process, the following step-by-step table organizes each phase with its corresponding key activities:
| Step | Key Activities |
| Assessment and Asset Mapping | Inventory assets, map data flows, identify risks |
| Implement Least Privilege Access |
Set role-based access, enable multi-factor authentication, manage permissions dynamically |
| Continuous Monitoring & Adaptive Security |
Deploy real-time analytics, automate threat detection, establish rapid incident response processes |
Zero Trust is not a one-time implementation but an ongoing process of verification and adaptation. Organizations must establish robust monitoring systems that track and analyze every network interaction in real-time. This means deploying advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms, and automated threat detection mechanisms that can instantly identify and respond to suspicious activities.
Critical components of continuous monitoring include:
- Real-Time Analytics: Tracking user behaviors and network interactions
- Automated Threat Detection: Using AI to identify potential security anomalies
- Rapid Incident Response: Creating predefined protocols for addressing security incidents
Successful Zero Trust implementation requires a cultural shift within an organization. It demands collaboration between IT security teams, leadership, and employees to create a unified approach to cybersecurity. This means investing in training, developing clear security policies, and fostering a mindset of continuous vigilance. Businesses must recognize that Zero Trust is not a destination but a journey. As technological landscapes evolve and cyber threats become more sophisticated, Zero Trust security frameworks must remain flexible, adaptive, and responsive to emerging challenges.
Benefits for Professionals and Enterprises
For modern professionals and enterprises, Zero Trust offers a transformative way to approach. By reimagining cybersecurity, organizations can achieve unprecedented levels of protection, efficiency and strategic resilience.
Enhanced Cybersecurity and Risk Mitigation
According to the U.S. Government Accountability Office, Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) provides exceptional data and system protection by authenticating and authorizing every single network interaction. This comprehensive approach significantly reduces potential security vulnerabilities by confining potential incidents and improving overall situational awareness.
Caltech’s research emphasizes that Zero Trust security dramatically reduces organizational attack surfaces. By implementing strict access controls and continuous verification, enterprises limit attackers’ opportunities to exploit system vulnerabilities. Professionals benefit from a more robust and adaptive security framework that anticipates and neutralizes potential threats before they can cause significant damage.
Operational Efficiency and Visibility
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency highlights that Zero Trust principles dramatically improve organizational visibility and threat understanding. This enhanced monitoring capability enables professionals to:
- Detect Threats Rapidly: Identify and respond to potential security incidents in real-time
- Automate Security Processes: Streamline threat detection and response mechanisms
- Gain Comprehensive Insights: Understand network interactions with unprecedented depth
Professionals can leverage these capabilities to transform cybersecurity from a reactive function to a proactive, strategic asset. The ability to continuously monitor and analyze network interactions provides unprecedented transparency into organizational digital ecosystems.
Flexible and Adaptive Security Strategies
Zero Trust security offers remarkable flexibility for modern enterprises operating in dynamic technological landscapes. Unlike traditional security models that rely on rigid perimeter defenses, Zero Trust adapts continuously to changing organizational needs and emerging threat landscapes.
Key advantages include:
- Remote Work Support: Seamless security for distributed workforce environments
- Scalable Protection: Security frameworks that grow alongside organizational complexity
- Compliance Enhancement: Robust mechanisms for meeting stringent regulatory requirements
For IT professionals and enterprise leaders, Zero Trust represents more than a technological solution. It’s a strategic approach that aligns cybersecurity with broader business objectives, enabling organizations to innovate confidently while maintaining robust digital protection. The future of cybersecurity lies in adaptive, intelligent frameworks that can anticipate and neutralize threats dynamically. Zero Trust security provides professionals and enterprises with the tools, strategies, and mindset necessary to navigate increasingly sophisticated digital risk landscapes effectively.
Ready to Make Zero Trust Real for Your Critical Operations?
Zero Trust is a critical step in building real-world defense by questioning every user, device and action. But what happens when hidden threats, like AI-generated attacks, slip through the cracks? Many organizations adopting Zero Trust still face the pain of insider risks, compliance headaches, and the new threat of adversarial AI or deepfake attacks that traditional tools miss. If your business relies on protecting sensitive data while staying fully compliant, your security needs to be as dynamic and adaptive as Zero Trust itself.
Now is the time to put your new Zero Trust understanding into action. Discover how Polygraf AI empowers your security framework with award-winning, locally deployed AI-native solutions. Identify AI and deepfake threats instantly, enforce compliance and defend against data leaks or LLM attacks. Visit Polygraf AI to see why we’re recognized for being a top AI Governance, Data Security and Data Provenance solution. Take the next step to real-world ZeroTrust and protect your business today.
About Polygraf AI:
Polygraf AI provides award-winning AI-native data integrity, monitoring & governance solutions to organizations via an on-prem, Zero Trust framework. As artificial intelligence advances, organizations face new risks from confidential data loss, data breaches, and fake or altered AI-generated content. Polygraf enables data-centric organizations to identify, monitor & and mitigate these emerging threats with its proprietary, agentic AI solutions. The company is headquartered in Austin, TX.
Ready to show customers and investors that your startup leads with credibility and security? Schedule a demo on Polygraf AI and see how you can strengthen your compliance edge today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity model that operates on the principle of ‘never trust, always verify.’ It requires continuous verification of users and devices before granting access, regardless of their location within or outside the organizational network.
What are the key principles of Zero Trust Security?
The key principles of Zero Trust Security include continuous verification of every interaction, implementing least privilege access controls and operating under the assumption that a security breach could occur at any time. This approach helps mitigate risks and enhance security.
How does Zero Trust Security protect businesses?
Zero Trust Security protects businesses by reducing the attack surface, enhancing visibility into network activities and enabling more efficient threat detection. It minimizes the potential damage from breaches by treating every access request as suspicious and requiring thorough validation.
What steps are involved in implementing Zero Trust Security?
Implementing Zero Trust Security involves several critical steps: assessing and mapping assets, enforcing least privilege access controls, and establishing continuous monitoring and adaptive security measures to respond to evolving threats.





